Tip-Growing Robots: Design, Theory, Application
Jul 1, 2025·
,
 ,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
·
0 min read
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
·
0 min read
Shamsa Al Harthy
S.M.Hadi Sadati
Cédric Girerd
Sukjun Kim
Alessio Mondini
Zicong Wu
Brandon Saldarriaga
Carlo A. Seneci
Barbara Mazzolai
Tania K. Morimoto
Christos Bergeles
Abstract
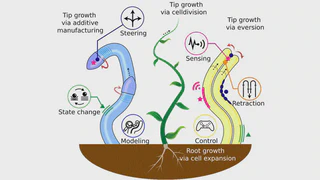
Growing robots apically extend through material eversion or deposition at their tip. This endows them with unique capabilities such as follow the leader navigation, long-reach, inherent compliance, and large force delivery bandwidth. Tip-growing robots can therefore conform to sensitive, intricate, and difficult-to-access environments. This review paper categorizes, compares, and critically evaluates state-of-the-art growing robots with emphasis on their designs, fabrication processes, actuation and steering mechanisms, mechanics models, controllers, and applications. Finally, the paper discusses the main challenges that the research area still faces and proposes future directions.
Type
Publication
Transactions on Robotics